The number of charging stations for electric vehicles is growing across Europe and Asia.
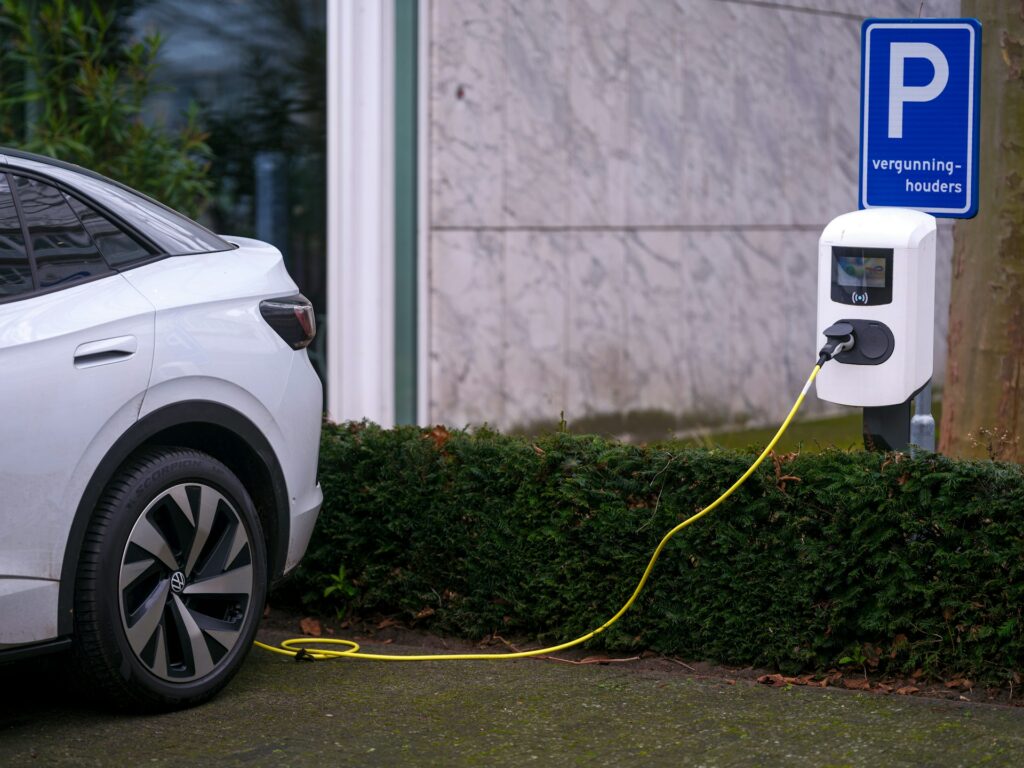

The number of charging stations for electric vehicles is growing across Europe and Asia.
In the year 2025, the proliferation of electric vehicle (EV) charging networks across Asia and Europe is causing a transformation in the transportation sector and is hastening the transition toward clean energy on a global scale. For the purpose of meeting the ever-increasing demand for electric mobility, governments, automobile manufacturers, and private energy businesses are making significant investments in large-scale infrastructure projects. An important turning point in the shift to environmentally friendly modes of transportation is the rapid development of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, which includes everything from ultra-fast charging lanes to smart stations powered by renewable energy sources.
1. The Worldwide Movement Towards Electricity Utilization
The shift away from fossil fuels and toward electricity is no longer a choice; rather, it is an unavoidable possibility. The continents of Asia and Europe have each established lofty decarbonization objectives for the year 2030 and beyond. The expansion of electric vehicle charging networks is a crucial step toward accomplishing these goals. The “range anxiety” that once slowed down the broad adoption of electric vehicles is being alleviated by the increasing availability of public and private charging sites, which is making electric vehicles more more accessible.
2. The Rapid Expansion of Europe’s Infrastructure Network
Due to stringent rules on emissions and customer incentives, Europe has emerged as a frontrunner in the deployment of electric vehicle charging stations. The Green Deal and the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) adopted by the European Union are providing money for the building of huge networks. By the year 2025, practically every major highway in Europe will be equipped with ultra-fast chargers that are spaced fewer than sixty kilometers apart, which will make traveling across borders easier for electric vehicles. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are among the countries that are in the forefront of the movement with dense networks that are powered by renewable energy.
3. The Quickening of the Electric Mobility Industry in Asia
Asia, which is home to some of the greatest automotive markets in the world, is experiencing a boom in electric vehicle infrastructure that is unparalleled. China has already established millions of charging stations and is experiencing significant expansion in both its urban and highway networks, making it the leader in this revolution. Japan and South Korea are concentrating their efforts on developing technologies that allow for rapid charging and battery swapping, while India is speeding the deployment of electric vehicles in urban centers as part of its national electrification projects. Mobility and energy consumption patterns in the region are being reshaped as a result of these trends collectively.
4. The Increasing Trend of High-Power Charging and Ultra-Fast Charging
The spread of ultra-fast chargers that are capable of supplying up to 350 kW of power is a significant technological advancement that will occur in the year 2025. This is sufficient to recharge the majority of electric vehicles to 80% in less than 15 minutes. These chargers of the next generation are quickly becoming the standard throughout major networks on both continents. Charging speeds are continuing to grow as battery technology continues to advance, which makes owning an electric vehicle more convenient than it has ever been before.
5. The incorporation of environmentally friendly energy sources
The electric vehicle charging revolution is centered on the concept of sustainability. Hydropower, solar power, and wind power are examples of renewable energy sources that are being included into charging infrastructure in both Europe and Asia. There are a lot of new stations that have solar panels and battery storage systems installed on-site, which helps to lessen reliance on the grid and provide a steady supply of energy. Consequently, this leads to an ecosystem that is cleaner and more efficient, in which automobiles are fuelled by the same renewable energy sources that are driving the move to a greener global economy.
6. Artificial intelligence-driven energy management and smart grids
Artificial intelligence and smart grid technology are playing an important part in the management of the increasing strain that electric vehicles are placing on electricity networks. Demand is monitored by systems driven by artificial intelligence, which also forecasts usage peaks and optimizes energy distribution across charging stations. A “dynamic load balancing” system that is powered by artificial intelligence helps to maintain grid stability during times of heavy demand in Europe. Meanwhile, predictive analytics are assisting utilities in Asia in planning charging expansion based on urban growth and traffic patterns.
7. Systems for Charging Vehicles Across Borders
Twenty-five years from now, one of the most important developments that will take place is the formation of international charging alliances. For the purpose of standardizing connections, payment systems, and network protocols, European initiatives such as “ChargeUp Europe” and Asian projects that fall under the ASEAN Smart Mobility Framework are also being undertaken. The capacity to charge electric vehicles (EVs) in a seamless manner between countries is made possible by interoperability, which in turn promotes regional connectivity and economic integration.
8. Collaboration Between the Public and Private Sectors
It is imperative that governments, automobile manufacturers, and private energy sources work together in order to ensure the success of the electrical vehicle infrastructure growth. Large-scale charging deployments are being driven in Europe by partnerships between Tesla and Ionity, as well as state utilities. Governments in Asia are collaborating with new businesses and established energy companies to set up stations in both urban and rural areas of the continent. These agreements are guaranteeing that the infrastructure is able to keep up with the rapid increase in the number of people using electric vehicles.
9. Integration of Smart City Technology and Powering Cities
metropolitan charging is becoming an increasingly important concern as the number of electric vehicles (EVs) in metropolitan areas continues to increase. Charging stations are being installed in public parking lots, shopping centers, and residential areas on both the American and European islands. Charger stations are connected to smart city platforms in cities such as Paris, Tokyo, and Singapore. These systems optimize energy use, monitor air quality, and even enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) energy sharing, which allows electric vehicles to flow electricity back into the grid during peak hours.
10. Recent Developments in Methods for Mobile Charging and Battery Swapping
In addition to the conventional method of plugging in a device, Asia is at the forefront of battery-swapping technology. An increasing number of businesses in China and India are putting in place automated stations that allow drivers to quickly replace batteries that have run out of power. While this is going on, Europe is conducting research and development studies on mobile charging vans and wireless induction pads for taxis and buses. By providing both flexibility and speed, these improvements broaden access to electric vehicle power, whether in regions that are densely populated or extremely isolated.
11. Repercussions on the Economy and the Environment
Both regions are experiencing an increase in economic activity and employment creation as a result of the expansion of charging infrastructure infrastructure. There is a significant increase in the construction industry, energy management, and digital service providers. When it comes to the environment, the decrease in emissions is considerable; each expansion of charging networks powered by renewable energy sources leads to cleaner air, less reliance on oil, and lower levels of urban pollution. The development of electric vehicle charging networks is becoming a symbol of progress toward a low-carbon and sustainable economy.
12. The Way Forward: A Future Characterized by Connected Electricity
It is anticipated that by the end of the year 2025, Asia and Europe will be home to the electric vehicle charging ecosystems that are the most widespread and technologically advanced in the entire world. Interoperability, the incorporation of renewable energy sources, and user ease are currently becoming the primary focuses. Eventually, electric mobility will no longer be an alternative; rather, it will become the standard for transportation all around the world as charging gets more efficient, cleaner, and more intelligent.
In the process of transitioning to sustainable energy, the spread of electric vehicle charging networks across Asia and Europe represents a significant step. Ultra-fast chargers, the incorporation of renewable energy sources, and energy management that is driven by artificial intelligence are redefining what is possible in sustainable mobility. It is expected that electric vehicles will become the dominant mode of transportation on roadways across all continents as governments and companies work together to establish a universal charging infrastructure. In the year 2025, the revolution in infrastructure will not only focus on powering automobiles; rather, it will also focus on powering the future of transportation itself.